INFORMATION AVAILABLE IN ENGLISH, GUJARATI AND HINDI
What is a hernia?
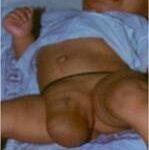
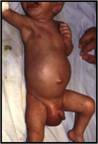
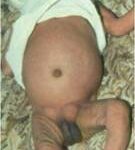
A hernia describes a small piece of abdominal lining, and sometimes a section of the bowel, which bulges out through the abdominal wall. Both children and adults can have hernias. Sometimes it is present at birth. The hernia can look bigger when your child cries or strains.
What causes a hernia?
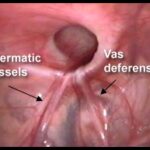
While your child was developing in the womb, the testicles were developing inside the abdomen. Towards the end of pregnancy, the testicle travel through a passage into the scrotum. When this passage fails to close the intestines in the abdomen tend to bulge out through it causing a hernia. Unlike adults, there is no generalized weakness of the abdominal wall that causes hernia in children. Sometimes the passage through which the testis has come down may be small allowing only fluid around the intestines to come down. This is called a ‘hydrocele’.
How common are hernias in children?
Hernias are more common in boys than girls. About one in 50 boys will have a hernia during their childhood. The condition is also more common in babies born prematurely.
Is it possible to prevent a hernia?
There is no known way of preventing a hernia.
How is a hernia diagnosed?
Your doctor will be able to diagnose the hernia by clinical examination as it appears as a characteristic lump in your child’s abdomen. Your child may not need any further diagnostic investigations.
How are hernias treated?
Your child will need a small operation. In many cases this can be carried out as day surgery – your child will arrive at the hospital, have the operation and be able to go home on the same day. Occasionally a child will need to stay in hospital for a day or two.
Hernias in children do not need placing a mesh or a net as is used in adult hernia repairs. The reason for this is that in children cause for the hernia is completely different than in adults where hernia is caused because of the weakness of the abdominal muscles.
At what age should the child have surgery for hernia?
Hernia should be operated earliest after the diagnosis, irrespective of your child’s age or weight. Untreated hernias are known to have complications in the form of obstruction where the intestine gets stuck and fails to go back in the abdomen. This will then require emergency treatment.
Remember: “SMALLER THE CHILD AND SMALLER THE HERNIA, GREATER THE RISK OF OBSTRUCTION.”
Children with obstructed hernias
What does the operation involve?
The operation is carried out under general anaesthetic and lasts for about 30 – 45 minutes. Once your child is asleep, the surgeon will make a small incision (cut) on the lower abdomen, The abdominal lining and piece of bowel will be pushed back into place. The open passage will be repaired and closed with stitches. These stitches will dissolve and will not have to be removed.
Can this operation done by laparoscopy?
Operation in hernia involves closing of the open passage through which the testis has come down. This can be done from outside as in open surgery or from inside by laparoscopy. If your child has got a hernia on one side, there is a 15 – 25 % chance that he / she may develop a hernia on the opposite side at a later date. With the help of laparoscopy we are able to look at the opposite side to see if the passage is open on that side as well. This can be closed at the same sitting if you wish to. Recovery from surgery, timing of surgery and discharge from hospital are the similar for open surgery and laparoscopic surgery.
However, it is important to note that an open passage does not always mean that your child will get a hernia. There is no harm in opting for a second surgery later if your child at all develops a hernia on the opposite side.
Laparoscopic repairs have a slightly higher chance of recurrence (i.e. the hernia coming back again) as compared to open hernias. You can discuss the pros and cons in details with your doctor when you come for consultation.
What are the risks of surgery?
After an anaesthetic some children may feel sick and vomit. They may have a headache, sore throat or feel dizzy. These side effects are usually short-lived and not severe. Some children develop swelling over the scrotum 24 hours after surgery. This gradually resolves on its own over the course of the next week.
What happens after the operation?
Your child will recover from the anaesthetic on the ward. Once he feels comfortable and has something to drink and eat, you will be able to take your child home. We recommend that you bring in some loose clothing for your child to wear home and for the next few days, as this will be a lot more comfortable.
What happens after you go home?
Your child should not have a bath or shower for three to five days after the operation. After this, it is fine for your child to have a shower, but try to avoid long baths as this may cause the scab to soften and fall off too early.
Your child should be ready to go back to school or nursery about a week after the operation.
The stitches will dissolve on their own within two weeks or so. You will need to visit hospital for a follow up check 7 – 10 days after surgery.
Are there any long term effects of hernia repair?
Most hernia repair operations are successful. You should see an immediate reduction or the complete disappearance of the hernia.
One out of ten children develops a hernia on the opposite side of the body. This risk is doubled if your child has been born prematurely.
GUJARATI
સારણગાંઠ અને વધરાવળ
સારણગાંઠ ૨% બાળકોમાં જાવા મળે છે. બાળક માઁના ગર્ભમાં હોય ત્યારે બાળકના પેટમાં વૃષણની ગોળી બને છે, અને આ ગોળી પેટની બહાર નીકળી અને વૃષણ કોથળીમાં આવે છે. બાળકના જન્મ દરમિયાન આ રસ્તો સામાન્ય રીતે બંધ થઈ જાય છે, પરંતુ જ્યારે આ રસ્તો બંધ નથી થતો ત્યારે આંતરડા બહાર આવે છે અને સારણગાંઠ થાય છે. જા રસ્તો નાનો હોય અને ફક્ત પેટનું પાણી જ બહાર આવે, તો તેને વધરાવળ કહેવાય છે.
સારણગાંઠનું આૅપરેશન નિદાન થયા પછી તુરંતજ, બની શકે તેટલું વહેલું કરી દેવું જાઈએ. સારણગાંઠના આૅપરેશન માટે બાળકની ઉંમર કે બાળકના વજન જેવા કોઈ પરિબળ હોતા નથી. સારણગાંઠનો આૅપરેશન સિવાય બીજા કોઈ ઇલાજ નથી.
સામાન્ય રીતે બાળકને તપાસતાજ સારણગાંઠ અને વધરાવળની ખબર પડી જાય છે, તેના માટે કોઈ વિશેષ તપાસની જરૂર હોતી નથી. સોનોગ્રાફી કરાવવાનો ફાયદો એટલોજ છે કે એક બાજુ સારણગાંઠ હોય તેવા બાળકને સામેની બાજુએ રસ્તો ખુલ્લો છે કે નહીં તે ખબર પડે.
બાળકોને સારણગાંઠના આૅપરેશનમાં ફક્ત આ ખુલ્લો રહી ગયેલો રસ્તો જ બંધ કરવાનો હોય છે. તેમાં મોટા માણસોની જેમ જાળી મૂકવાની જરૂર હોતી નથી. સારણગાંઠનું આૅપરેશન જા ન કરવામાં આવે તો ૧૦% થી ૧૫% બાળકોમાં આંતરડું ફસાવાની શક્યતા રહેલી છે જે એક સીરિયસ પ્રોબ્લેમ છે. સારણગાંઠનું આૅપરેશન નિદાન બાદ બને તેટલું વહેલું કરાવવું જાઈએ. આથી વિપરીત બાળક ૧ વર્ષનું થાય ત્યાં સુધી વધરાવળ આપમેળે મટવાની શક્યતા રહેલી છે. •
HINDI
हर्निया और हाइड्रोसील
हर्निया और हाइड्रोसील एक आम्ा बि्ाम्ारी है जो २% ब्ाच्चों म्ों देखी जाती है। बच्चों में हर्निया और हाइड्रोसील का कारण मार्ग की आशंका है जिसके साथ वृषण पेट से निकल कर अंडकोश में आते हैं। ग्ाभ्ार् म्ों ब्ाच्चे के विकास के दौरान पेट के संकुचित म्ाग्ार् से आँत और पानी अंडकोष की थैली म्ों उतरता है, जिससे हर्निया और अंडकोष वृद्धि (हाइड्रोसील) की सम्ास्या होती है।
हर्निया और हाइड्रोसील की पहचान केवल चिकित्सीय परीक्षण द्वारा की जा सकती है। इसके लिए कोई विशेष जांच की आवश्यकता नहीं है। हालांकि, विपरीत दिशा में ट्रैक्ट की पेटेंसी को देखने के लिए अल्ट्रासाउंड स्कैन किया जा सकता है। इनगुनल हर्निया की पहचान होते ही बच्चे की आयु या उसके वजन की परवाह किये बिना जल्द से जल्द इसकी सर्जरी की जानी चाहिए। यदि हर्निया का इलाज समय पर न किया जाए तो आँतों में रूकावट या ऐंठन जैसी जटिलताएँ हो सकती है। साम्ान्यतः हर्निया से विपरीत, हाइड्रोसील १ वर्ष की उम्ा्र तक अपने आप ठीक हो जाता है, लेकिन १ वर्ष की उम्ा्र के ब्ाद ब्ाच्चे म्ों हाइड्रोसील की सम्ास्या रहने पर सर्जरी कराना आवश्यक है। सर्जरी (हर्नियोटॉमी) द्वारा पेटेंट स्थान को बंद कर दिया जाता है। वयस्कों की भांति बच्चों में जाली लगाने की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है। यह प्रक्रिया आमतौर पर एक दिन की देखभाल में की जाती है, जहाँ बच्चे को सुबह अस्पताल में भर्ती किया जाता है और शाम को घर भेज दिया जाता है। •