INFORMATION AVAILABLE IN ENGLISH, GUJARATI AND HINDI
What is hydrocephalus?
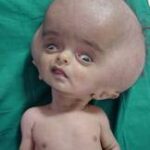
Hydrocephalus occurs when either too much cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is produced (very rare) or when it is stopped from circulating or being re-absorbed. The CSF builds up within the ventricles (cavities) of the brain resulting in increased pressure on the brain. In babies, this also causes the head to enlarge.
CSF is a watery liquid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, acting as a ‘cushion’. It also supplies nutrients to the brain.
What causes hydrocephalus?
The most common causes are:
- Congenital – This means that your child was born with hydrocephalus. Children born with spina bifida often develop hydrocephalus. This does not mean that all children with hydrocephalus also have spina bifida.
- Prematurity – Hydrocephalus can occur as a complication of being born too early, and when there has been bleeding in the brain.
- Meningitis – Hydrocephalus can occur as a complication of meningitis as the infection may cause a problem with reabsorption of CSF.
- As a complication from a brain tumour – this does not mean children with hydrocephalus develop brain tumours.
- Unknown – In many cases, we do not know what caused the hydrocephalus.
How is hydrocephalus diagnosed?
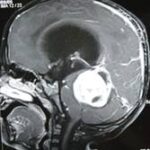
It is usually diagnosed by an increasing head circumference in infants, an ultrasound scan, a CT scan or sometimes an MRI scan.
How is hydrocephalus treated?
If hydrocephalus is not treated, your child’s head would get larger and the pressure on the brain would interfere with his or her development. In severe cases, this can result in permanent brain damage or visual problems. The aim of treatment is to reduce the pressure on the brain by draining the CSF away.
The fluid is drained away using a ‘shunt’, which is a long tube made of silicone. It is inserted in to the ventricles in an operation and drains the CSF away to the abdomen. The shunt contains a valve so that the fluid can only drain away from the head at the desired rate.
The operation
Part of your child’s hair, behind the ear, will be shaved and he or she will have an incision (cut) there in a horseshoe shape and a small incision on his or her abdomen.
Your child will have this operation under a general anaesthetic. The operation takes about 45 min to an hour. At the time of surgery fluid that is drained from the brain will be sent to the laboratory for examination.
What happens after the operation?
Close observation will be needed following surgery. Most children are able to take oral feeds the same evening of the operation. The usual stay in hospital is four to six days.
To begin with, the area around the top of the shunt may be slightly raised, but as the swelling settles and your child’s hair grows back you will not notice this. As your child grows, the area will become less prominent.
Going home
Your child may have dissolvable stitches or they may have stitches that need to be removed seven days after the operation.
Complications of a shunt
There can be complications to having a shunt inserted, of which you should be aware. The most common could be either an infection or a blocked shunt.
Symptoms of Infection
The symptoms of an infection in the shunt may include:
- Headache
- Irritability
- High temperature (over 37°C)
- Not feeding well
- Possibly vomiting
- Possibly drowsy
Symptoms of a blocked shunt
In babies:
- A bulging fontanelle (soft part of the top of the head)
- Vomiting
- Crying and irritability
- Becoming sleepy (less responsive)
- Looking pale
- Increased head size
In toddlers and children:
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Tiredness
- Drowsy
- Looking pale
GUJARATI
માથું મોટું હોવું
બાળકનું માથું મોટું હોવું એક ચિંતાનો વિષય જરૂર છે, અને તેનાં માટે ડાક્ટરની સલાહ જરૂરી છે. જન્મથીજ ડાક્ટર માથું અને છાતીના માપનો રેકોર્ડ રાખે છે અને તેને સ્ટાન્ડર્ડ ચાર્ટ સાથે સરખાવે છે. તેના પ્રમાણે સતત વધતાં માથા માટે જરૂરી તપાસ કરાવવી પડે છે.
માથું મોટું થવાનું સૌથી મુખ્ય કારણ નવજાત બાળકોના મગજની અંદર આવેલ પાણી (C.S.F.) નો ભરાવો છે. જેને હાઈડ્રોકેફલસ કહે છે. આમાં બાળકનું માથું નિયમિત ગતિથી વધ્યાં કરે છે. બીજા કારણોમાં બાળકને જન્મ પછી બ્રેન હેમરેજ થયું હોય તો પણ માથું મોટું થાય છે. જ્વલ્લે જ બાળકને બ્રેન કેન્સર જેવી બીમારીથી માથું મોટું થઈ શકે છે.
હાઈડ્રોકેફલસ સૌથી સામાન્ય કારણ છે. અને તેનું સચોટ નિદાન નાના બાળકોમાં સોનોગ્રાફી દ્વારા અને મોટા બાળકોમાં સી.ટી.સ્કેન અથવા એમ.આર.આઈ.થી થઈ શકે છે.
બાળકોનાં સર્જન આવા કેસમાં એક શંટ મૂકવાની સલાહ આપે છે જેમાં એક પાતળી ટ્યુબ દ્વારા માથાના વધારાના પાણીને પેટમાં ડાયવર્ટ કરાય છે. આ ટ્યુબને વી.પી. શંટ કહે છે.તેનું રેગ્યુલર ચેકઅપ કરાવતાં રહેવું જરૂરી છે. •
HINDI
बडा सिर (जल शीर्ष)
बच्चे के सिर का बड़ा होना चिंता का विषय जरुर है और इसके लिए डॉक्टर से परामर्श जरुरी है। बच्चे के जन्म लेते ही डॉक्टर उसके सिर तथा छाती के माप का रिकार्ड रखते है और उसकी तुलना मानक चार्ट से करते रहते हैं। अगर सिर के माप में निरंतर वृद्धि हो तो जाँच आवश्यक होती है।
इसका प्रमुख कारण नवजात शिशु के मस्तिष्क में जल भराव (C.S.F.) जिसे हाइड्रोसीफेलस कहते हैं। इसमें बच्चे का माथा नियमित गति से बढ़ता रहता है। इसका दूसरा कारण जन्म के समय बच्चे को ब्रेन हेमरेज होना भी हो सकता है। ब्रेन कैंसर जैसी बीमारी के कारण सिर का बड़ा हो जाना बच्चों में कम ही पाया जाता है।
हाइड्रोसीफेलस एक सर्वसामान्य कारण है। बच्चों के मामले में इसका सटीक निदान सोनोग्राफी के द्वारा तथा वयस्कों में सी.टी. स्कैन अथवा एम.आर.आई के द्वारा किया जाता है।
बालरोग सर्जन ऐसे मामलों में एक सादा सा शंट लगाने की सलाह देते हैं। इस प्रक्रिया में एक नलीका के माध्यम से माथे का पानी पेट में डायवर्ट किया जाता है। इस नलिका को वी.पी. शंट कहते हैं। इस में नियमित चेकअप की आवश्यकता होती है। •